Corporate Update: Rocket Lab Corporation (NASDAQ: RKLB) – Recent Testing Incidents, Earnings Outlook, and Industry Context
1. Overview of Recent Testing Activity
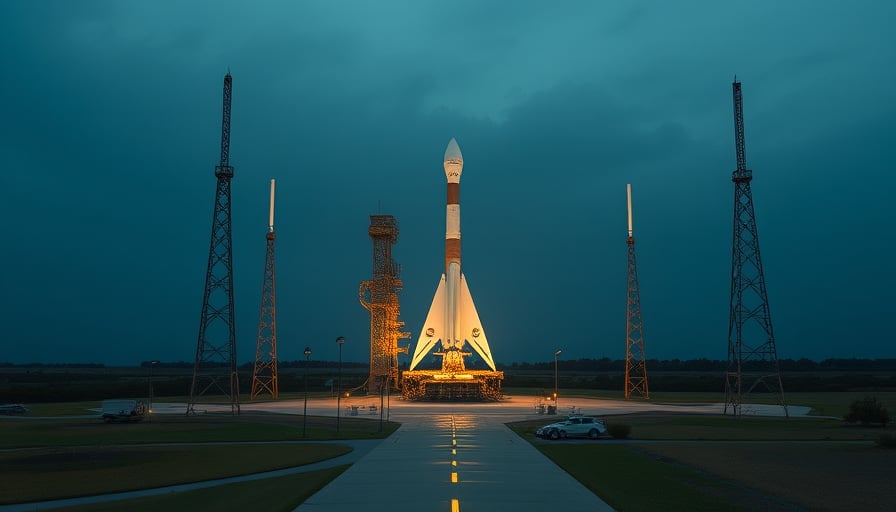
Rocket Lab Corporation, the American aerospace company specializing in small‑satellite launch services, has announced a rupture during a hydrostatic pressure test of the first‑stage tank of its Neutron rocket. The test, conducted as part of the vehicle’s qualification program, was halted to allow for a detailed investigation into the failure. Company representatives emphasized that such anomalies are a normal part of rigorous testing regimes and that the incident did not inflict substantial damage on the test rig.
From an engineering standpoint, hydrostatic pressure tests validate the structural integrity of propellant tanks under conditions that exceed the expected operational loads. A rupture in this context typically signals an over‑pressure scenario, a failure of a weld, or a material defect that may have gone undetected during manufacturing or non‑destructive evaluation. While the immediate impact on the test infrastructure was limited, the event underscores the iterative nature of rocket development, where each fault analysis informs subsequent design refinements and quality‑control adjustments.
2. Financial Performance and Analyst Expectations
2.1 Quarterly Results and Forecast
Rocket Lab’s latest earnings report signals a modest loss for the current quarter, with analysts projecting a similar trajectory for the full fiscal year. The company’s revenue growth has remained constrained by the limited launch cadence of the Neutron vehicle and the ongoing ramp‑up of its manufacturing pipeline. Costs associated with research and development, propellant procurement, and facility expansion have continued to outweigh revenue inflows, a pattern typical of aerospace firms in the early‑stage commercial launch market.
2.2 Credit Rating and Price Target Adjustments
Goldman Sachs maintained a neutral rating on Rocket Lab’s stock while revising its price target to reflect the company’s current valuation metrics and the broader risk profile of the small‑satellite launch segment. The rating decision takes into account the company’s strong brand presence, the growing demand for low‑cost, high‑frequency launches, and the competitive pressure from larger players such as SpaceX and emerging entrants like Astra and Firefly.
3. Strategic Implications in the Defense and Manufacturing Landscape
3.1 Domestic Defense Procurement and Manufacturing Resilience
The U.S. Department of Defense has recently outlined a domestic procurement program aimed at bolstering manufacturing resilience for critical defense technologies. This initiative encourages the development of local supply chains for propulsion systems, avionics, and advanced materials. While Rocket Lab’s primary focus remains commercial satellite launch services, its involvement in the Neutron program positions the company to potentially supply propulsion components or related technology to defense contractors.
Although no direct financial impact from the new defense procurement program has been reported for Rocket Lab, the company’s existing capabilities—such as rapid production of lightweight, high‑performance propulsion stages—align with the procurement program’s objectives. Strategic partnerships or supply agreements could emerge as the defense sector seeks to diversify beyond traditional aerospace suppliers.
3.2 Cross‑Sector Synergies and Broader Economic Trends
Rocket Lab’s situation exemplifies the broader trend of vertical integration in the aerospace industry, wherein firms combine design, manufacturing, and launch operations to achieve cost efficiencies and rapid innovation cycles. This model mirrors similar developments in the semiconductor and electric vehicle sectors, where end‑to‑end manufacturing is leveraged to reduce supply chain complexity and accelerate time‑to‑market.
Economic indicators such as rising interest rates, supply‑chain bottlenecks, and geopolitical tensions are influencing the capital allocation decisions of both private investors and defense agencies. Companies that can demonstrate resilience in their manufacturing processes—through modular design, redundant supply lines, and robust quality assurance—are likely to attract investment and contractual opportunities, irrespective of their immediate profitability.
4. Conclusion
Rocket Lab’s recent hydrostatic test rupture highlights the inherent risks of advanced rocket development but also reflects the disciplined approach required to achieve flight‑ready qualification. While the company’s current earnings outlook remains modest, the strategic alignment of its technology with emerging defense procurement priorities may provide future upside. Investors and industry analysts should monitor how Rocket Lab translates its engineering achievements into commercial and defense market opportunities, while also tracking its ability to navigate the evolving macroeconomic landscape that shapes capital investment in aerospace and related high‑tech sectors.